

How do You observe ?
By what sense do You prefer to observe ?
What do You observe ?
members of G1 move to the left and members of G2 move to the right.

DALL-E/GPT4o prompt: Provide black and white illustration of your response regarding unsupervised learning of music tunes into music genre clusters, in style of Gustav Doree
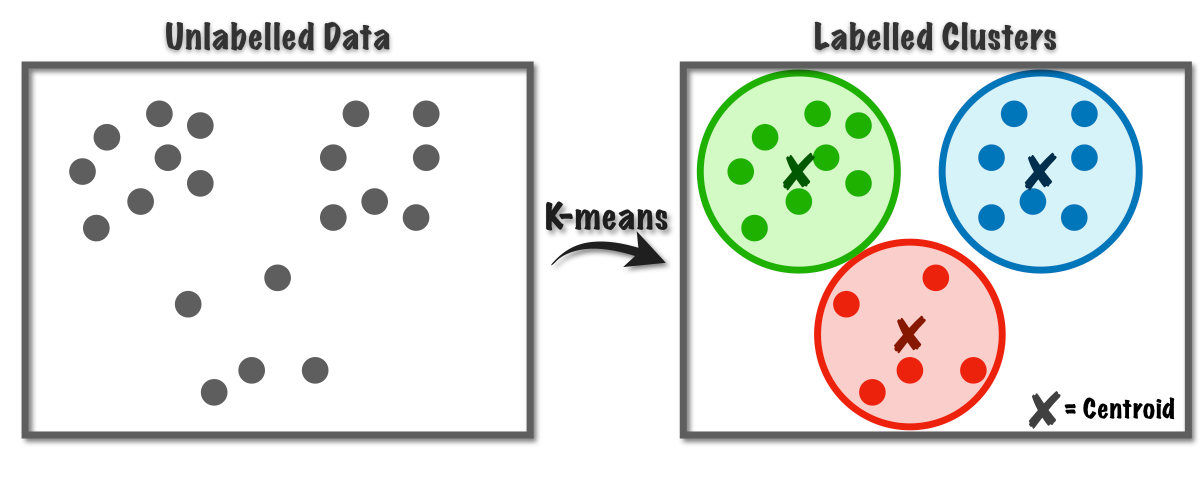
Can You think of other examples of unsupervised learning and/or clustering ?
No direct guidance :: Learner L must identify patterns or relationships from raw input on her own.
Pattern discovery :: Observation often involves recognizing and understanding patterns in the environment, which mirrors what happens in unsupervised learning.
Learning from the environment :: L derives insights from the world or data without external labels or supervision.

